Gazebos are popular outdoor structures used for various purposes, such as relaxation, entertainment, and dining. However, with the occurrence of thunderstorms and lightning strikes, concerns about the safety of gazebos arise.
Lightning is a natural phenomenon that can cause significant damage to structures and harm individuals if proper safety precautions are not taken.
The safety of gazebos in lightning depends on various factors, such as construction materials, location, and lightning protection systems.
While metal gazebos can act as a conductor of lightning, wooden gazebos are less conductive and can be safer in lightning strikes.
The location of the gazebo is also a critical factor as it should not be placed in an elevated or exposed area prone to lightning strikes. Additionally, installing lightning protection systems such as lightning rods can significantly increase the safety of gazebos during thunderstorms.
In this article, we will discuss the safety considerations for gazebos during lightning strikes and provide recommendations for ensuring the safety of individuals using gazebos in outdoor settings.
Are gazebos safe in lightning: Gazebos are unsafe during lightning storms due to their open structure and lack of grounding. They offer little protection, making them a risky place to seek shelter. It’s essential to seek a safer location indoors during thunderstorms.
Are gazebos safe in lightning?

Lightning can strike any structure, including gazebos because it’s not choosy. The taller the structure and the more open the space, the more likely it is to get hit.
Gazebos are often made of materials that can conduct electricity, such as metals like aluminum, copper, and steel.
Even if they are grounded, gazebos are still not completely safe during a lightning storm. It’s not a good idea to seek shelter in a gazebo during a lightning storm.
What is lightning?
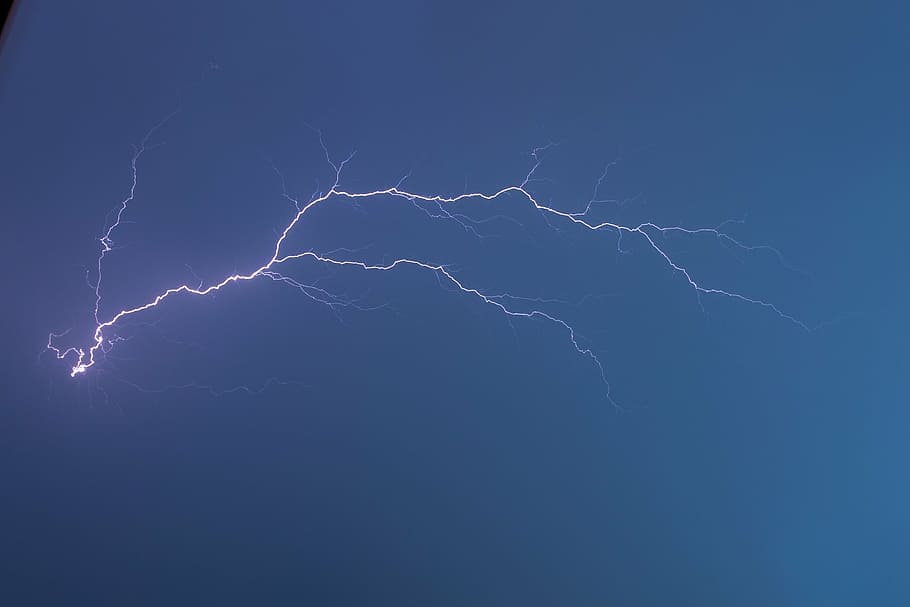

Lightning is a discharge of electrical energy that occurs in the atmosphere. It is caused by the buildup of static electricity generated by the movement of air currents and the separation of charges within clouds.
When the electrical charge in a cloud becomes too great, it will seek to discharge to the ground, creating a lightning bolt.
Many different types of lightning exist, including cloud-to-ground, intra-cloud, and cloud-to-cloud lightning. Cloud-to-ground lightning is the most common type, and it occurs when a bolt of lightning travels from a cloud to the ground.
Intra-cloud lightning occurs within a cloud, while cloud-to-cloud lightning occurs between different clouds.
How lightning strikes occur
Lightning strikes occur when there is a buildup of static electricity within a cloud. Several factors, including atmospheric instability, temperature differences, and the movement of air currents can cause this.
When the electrical charge within a cloud becomes too great, it will seek to discharge to the ground.
The discharge of electricity from the cloud to the ground is a lightning bolt. Lightning bolts are mighty and can travel up to 220,000 miles per hour.
When a lightning bolt strikes the ground, it can produce temperatures of up to 30,000 degrees Celsius, which is hotter than the sun’s surface.
Common myths about lightning
Many myths and misconceptions about lightning have been passed down through the generations. Here are a few of the most common:
Myth 1: Lightning never strikes the same place twice
This is a common myth, but it’s not true. Lightning can strike the same place multiple times, mainly if it’s a tall, pointed object like a tree or a lightning rod.
Myth 2: Lightning only strikes tall objects
While it’s true that tall objects are more likely to be struck by lightning, it’s not the only factor. Lightning can strike any object that provides a path of least resistance between the cloud and the ground. This includes buildings, cars, and people.
Myth 3: Rubber shoes and tires protect you from lightning
Rubber is an insulator, which means it doesn’t conduct electricity. However, if you’re standing on a surface that conducts electricity, like wet grass or metal, rubber shoes won’t protect you from a lightning strike. Similarly, rubber tires on a car won’t protect you if the car is struck by lightning.
Myth 4: If you’re caught in a thunderstorm, you should seek shelter under a tree
This is a dangerous myth. Trees are tall objects, and they attract lightning strikes. If you’re caught in a thunderstorm, you should seek shelter in a fully enclosed building or a car with a metal roof and windows closed.
Myth 5: Lightning only strikes during thunderstorms
While thunderstorms are the most common time for lightning strikes, they can happen anytime. Some types of lightning, like heat lightning, can occur without any visible signs of a thunderstorm.
Risks of using a gazebo during a thunderstorm

Gazebos are a popular outdoor structures used for various purposes, such as relaxation, entertainment, and dining.
However, with the occurrence of thunderstorms and lightning strikes, concerns about the safety of gazebos arise.
Lightning is a natural phenomenon that can cause significant damage to structures and harm individuals if proper safety precautions are not taken.
We will discuss the potential risks of using a gazebo during a thunderstorm, the dangers of lightning to the structure of a gazebo, and the risks of injury or death to people inside the gazebo.
Potential dangers of being in a gazebo during a thunderstorm
Gazebos are typically made of wood, metal, or vinyl and can have roofs made of fabric, shingles, or metal.
During a thunderstorm, the structure of a gazebo can become a lightning rod, attracting lightning strikes and posing a risk to individuals inside. The potential dangers of being in a gazebo during a thunderstorm include:
Direct lightning strikes
If lightning strikes the gazebo directly, the individuals inside can be severely injured or killed. Direct strikes can cause burns, cardiac arrest, and other serious injuries.
Indirect lightning strikes
Even if lightning strikes nearby, the electric current can travel through the ground and conductive materials, such as metal or water, and cause injury or death to individuals inside the gazebo.
Falling debris
Lightning strikes can cause debris, such as tree limbs or roofing materials, to fall onto the gazebo and injure individuals inside.
Wind damage
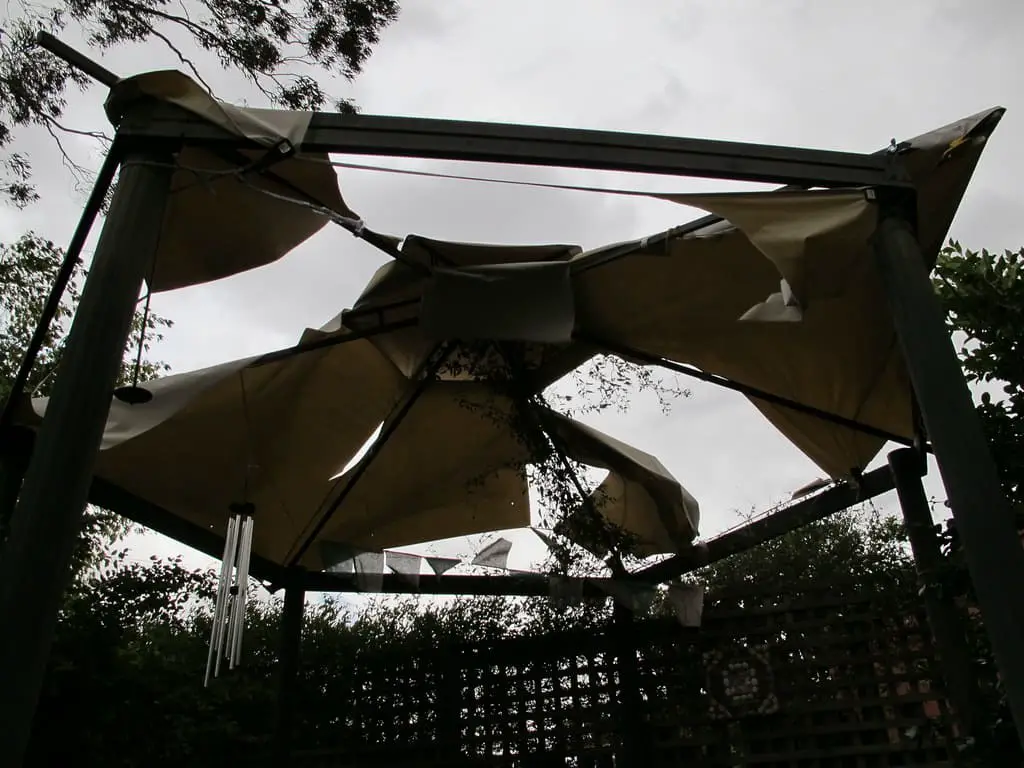

Thunderstorms are often accompanied by strong winds that can cause damage to the structure of a gazebo, making it unstable and posing a risk to individuals inside.
How lightning can affect the structure of a gazebo:
Lightning can cause significant damage to the structure of a gazebo, depending on the materials used and the location of the gazebo. Some of the ways lightning can affect the structure of a gazebo include:
Fire
Lightning can start fires in wood or vinyl gazebos, which can spread quickly and cause extensive damage.
Structural damage:
Lightning can cause structural damage to the gazebo, including cracks, splits, or collapses. Metal gazebos are particularly vulnerable to lightning strikes, as they can conduct electric current and cause damage to the structure.
Electrical damage
If the gazebo has electrical wiring or appliances, lightning can cause damage to the electrical system and pose a risk of electrocution to individuals inside.
Risks of injury or death to people inside the gazebo
Individuals inside a gazebo during a thunderstorm are at risk of injury or death due to lightning strikes or falling debris.
Additionally, if the storm damages the gazebo, it can become unstable and pose a risk of collapse or injury.
To minimize the risks of injury or death to individuals inside a gazebo during a thunderstorm, it is essential to take appropriate safety measures, including:
Evacuate the gazebo:
The safest option during a thunderstorm is to evacuate the gazebo and seek shelter indoors or in a vehicle. If there is no safe shelter nearby, it is best to move to a low-lying area and crouch down, minimizing contact with the ground.
Avoid contact with conductive materials:
If evacuation is impossible, individuals should avoid contact with conductive materials such as metal, water, or electrical wiring.
They should also avoid using electronic devices such as smartphones or tablets, as they can attract lightning.
Install lightning protection systems:
Installing lightning rods or surge protectors can help protect the structure of a gazebo from lightning strikes and minimize the risks of injury or death to individuals inside.
Factors that affect the safety of a gazebo during a thunderstorm

Gazebos are popular outdoor structures used for various purposes such as relaxation, entertainment, and dining.
However, with the occurrence of thunderstorms and lightning strikes, concerns about the safety of gazebos arise.
The safety of a gazebo during a thunderstorm depends on several factors, including the material and construction of the gazebo, the location of the gazebo, the surrounding environment, and the weather conditions. In this article, we will discuss these factors in more detail.
Material and construction of the gazebo
The material and construction of the gazebo can significantly impact its safety during a thunderstorm.
Different materials have different conductive properties and can attract lightning strikes differently. Some of the factors to consider include:
Wood gazebos
Wood is a poor conductor of electricity, making wooden gazebos less likely to attract lightning strikes. However, wood is also combustible and can catch fire if lightning strikes.
Metal gazebos

Metal is a good conductor of electricity, making metal gazebos more likely to attract lightning strikes.
If a metal gazebo is struck by lightning, the electric current can travel through the structure and pose a risk to individuals inside.
Vinyl or fabric gazebos
Vinyl or fabric gazebos are less conductive than metal gazebos but more conductive than wood gazebos.
If a vinyl or fabric gazebo is struck by lightning, the electric current can travel through the material and pose a risk to individuals inside.
In addition to the material of the gazebo, the construction of the gazebo can also impact its safety during a thunderstorm.
A well-constructed gazebo with proper grounding and lightning protection systems can minimize the risks of injury or damage.
Location of the gazebo
The location of the gazebo is another critical factor in determining its safety during a thunderstorm. The ideal location for a gazebo should be away from tall trees, power lines, and other conductive structures. Some other factors to consider include:
Elevation
Avoid placing the gazebo on elevated areas such as hills, ridges, or high ground, as they are more likely to attract lightning strikes.
Proximity to water
Avoid placing the gazebo near bodies of water such as lakes, rivers, or swimming pools, as they can increase the risk of injury or death if struck by lightning.
Shelter
If possible, choose a location that provides natural shelter, such as under a canopy of trees or in a covered patio. The natural shelter can provide some protection from the rain and wind during a thunderstorm.
Surrounding environment:
The surrounding environment can also impact the safety of a gazebo during a thunderstorm. Some of the factors to consider include:
Trees
Tall trees can attract lightning strikes and pose a risk of falling debris. Avoid placing the gazebo near tall trees or prune trees around the gazebo to reduce the risks.
Power lines
Avoid placing the gazebo near power lines, as they can conduct electricity and pose a risk of injury or death if lightning strikes.
Other conductive structures
Avoid placing the gazebo near other conductive structures such as metal fences or buildings, as they can attract lightning strikes and pose a risk to individuals inside the gazebo.
Weather conditions:
The weather conditions during a thunderstorm can also impact the safety of a gazebo. Thunderstorms are often accompanied by strong winds, heavy rain, and hail, which can cause damage to the structure of the gazebo and pose a risk to individuals inside. Some of the factors to consider include:
Wind speed
High wind speeds can cause the gazebo to become unstable and pose a risk of collapse or injury to individuals inside.
Rain and hail

Heavy rain and hail can cause damage to the gazebo’s roof and walls, compromising its structural integrity.
Frequency and severity of lightning strikes:
The frequency and severity of lightning strikes in the area can also impact the safety of a gazebo.
Areas with high lightning activity are more likely to experience a direct strike, which can cause significant damage to the gazebo and pose a risk to individuals inside.
Tips for staying safe in a gazebo during a thunderstorm
Gazebos are a popular outdoor feature that provides shade and shelter from the sun and rain. However, gazebos can pose a risk to those seeking refuge during a thunderstorm. Here are some tips for staying safe in a gazebo during a thunderstorm.
Preventive measures to take before a thunderstorm
Before a thunderstorm, it’s important to take preventive measures to reduce the risk of a lightning strike.
Here are some steps you can take:
Check the weather forecast
Keep an eye on the weather forecast and avoid using the gazebo if there’s a chance of thunderstorms.
Disconnect electrical appliances
If you have any electrical appliances in the gazebo, such as lights or fans, disconnect them before the storm arrives.
Secure loose items
Ensure any loose items, such as furniture or decorations, are secured or brought inside to prevent them from being blown around by strong winds.
Seek shelter in a fully enclosed building.
If possible, seek shelter in a fully enclosed building during thunderstorms to ensure your safety.
What to do if you’re caught in a gazebo during a thunderstorm
If you’re caught in a gazebo during a thunderstorm, it’s important to take the following steps to reduce the risk of a lightning strike:
Stay away from metal components
Lightning can travel through metal, so it’s important to avoid any metal components in the gazebo, such as metal chairs or tables.
Avoid contact with the ground:
Lightning can also travel through the ground, so avoiding contact with the ground as much as possible is important. If the gazebo sits on a concrete pad, stand on a non-conductive material, like a rubber mat or a wooden board.
Don’t touch other people.
If you’re with other people in the gazebo, don’t touch them. If lightning strikes the gazebo, the current can travel through your body and cause severe injury or even death.
Stay away from windows and doors.
If the gazebo has windows or doors, stay away from them during the storm. If lightning strikes the gazebo, the glass can shatter and cause injury.
Crouch down
If you can’t leave the gazebo, crouch on the ground with your feet close together. This will reduce your risk of being struck by lightning.
How to reduce the risk of a lightning strike
Here are some additional steps you can take to reduce the risk of a lightning strike:
Use a lightning rod
If the gazebo is equipped with a lightning rod, it will divert lightning strikes away from the gazebo and into the ground.
Stay informed
Monitor the weather forecast and avoid using the gazebo during thunderstorms.
Seek shelter in a fully enclosed building.
If possible, seek shelter in a fully enclosed building during thunderstorms to ensure your safety.
Use a surge protector.
If you have any electrical appliances in the gazebo, such as lights or fans, use a surge protector to protect them from power surges caused by lightning strikes.
Don’t take chances.
If you’re unsure about the safety of the gazebo during a thunderstorm, don’t take chances. Seek shelter in a fully enclosed building to ensure your safety.
FAQs
Q.1 Are gazebos safe during lightning?
Gazebos can be unsafe during lightning, as they often have metal components and are typically not fully enclosed structures.
Q.2 Why are gazebos unsafe during lightning?
Lightning can travel through metal and strike any object taller than its surroundings. Gazebos, which are often elevated and have metal components, can attract lightning and increase the risk of a lightning strike.
Q.3 Can lightning strike a gazebo?
Yes, lightning can strike a gazebo. If the gazebo has metal components, such as a metal roof or metal chairs, it can attract lightning and increase the risk of a lightning strike.
Q.4 How can I reduce the risk of a lightning strike in a gazebo?
To reduce the risk of a lightning strike in a gazebo, you can take several precautions, including disconnecting any electrical appliances, avoiding contact with metal components, seeking shelter in a fully enclosed building, and staying informed about the weather forecast.
Q.5 What should I do if I’m in a gazebo during a thunderstorm?
If you’re in a gazebo during a thunderstorm, it’s important to stay away from metal components, avoid contact with the ground, stay away from windows and doors, and crouch down on the ground with your feet close together. If possible, seek shelter in a fully enclosed building.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gazebos are not safe during lightning storms. Lightning is a compelling natural phenomenon that can cause severe damage and significantly threaten human life.
Understanding the nature of lightning and dispelling common myths can help people make informed decisions about staying safe during thunderstorms.
Gazebos are unsafe because they do not provide adequate protection against lightning strikes, and being inside a gazebo during a thunderstorm can expose people to potential dangers, such as electrocution and falling debris.
Factors such as the location of the gazebo and the presence of other conductive structures can also affect its safety during a thunderstorm.
Therefore, taking precautionary measures before a storm and seeking shelter if caught in a gazebo during a thunderstorm is crucial.
Following these precautions can significantly reduce the risk of injury or death from lightning strikes.
After reading this detailed guide on whether gazebos are safe during lightning storms, we hope you understand the risks and precautions well.
If you have any questions, please ask in the comments section.