Many homeowners and garden enthusiasts often consider using a gazebo as a greenhouse to grow plants and vegetables year-round. A gazebo is a structure typically used for outdoor entertainment, and it is often made of wood or metal with an open roof and sides.
However, the question arises, can a gazebo be used as a greenhouse? The answer is not straightforward. While a gazebo can provide shelter and protection from the elements, it is not specifically designed for growing plants.
On the other hand, a greenhouse is designed with specific features to regulate temperature, humidity, and ventilation to create an optimal environment for plant growth.
Despite this, some people have successfully converted their gazebos into greenhouses by adding modifications such as insulation, heating, and ventilation systems. With the right modifications, a gazebo can provide an excellent alternative to traditional greenhouses.
In this article, we will explore the benefits and drawbacks of using a gazebo as a greenhouse and the modifications necessary to make it work.
Can a gazebo be used as a greenhouse: A gazebo can be repurposed as a makeshift greenhouse by modifying it with transparent walls and roof materials. However, its original design might not provide optimal conditions for plant growth compared to a purpose-built greenhouse.
Explanation of a gazebo and greenhouse
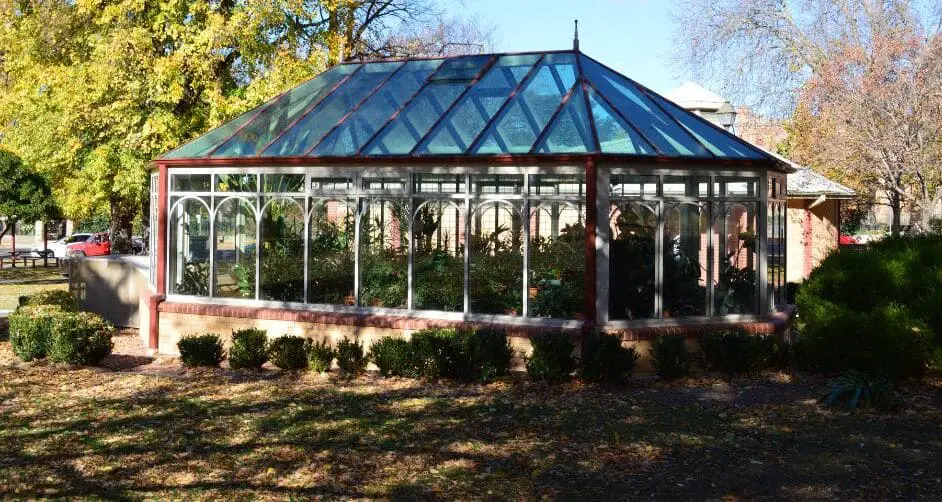

A gazebo is an outdoor structure that is typically roofed and open on all sides. It is often built as a standalone feature in a garden or park and is used as a place for relaxation or socializing. Gazebos can be made from various materials such as wood, metal, or vinyl.
On the other hand, a greenhouse is a structure used for growing plants, usually made of glass or other transparent materials, to allow sunlight to enter and create a controlled environment for plants to thrive.
Greenhouses are designed to maintain specific temperatures, humidity, and ventilation to optimize plant growth. They are often used for commercial plant production or for home gardening purposes.
A gazebo is an outdoor structure that is usually freestanding, with a roof and open on all sides. It can be found in gardens, parks, and other outdoor areas. Gazebos have been around for centuries, and their popularity has continued to grow due to their functional and aesthetic value.
This article we will provide an overview of gazebos, including their definition, types, and materials used in their construction.
Definition of a gazebo
A gazebo is a type of outdoor structure typically found in gardens, parks, and other outdoor spaces. It is often freestanding and has a roof and open sides. The roof of a gazebo can be flat, sloping, or domed, and it may be made of different materials such as wood, metal, or vinyl.
The open sides of a gazebo allow people to enjoy the surrounding environment and provide a sheltered space for relaxation, entertainment, or socializing.
Types of gazebos
There are different types of gazebos, each with its unique design and functionality. Some of the most common types of gazebos include:
Pavilion gazebos
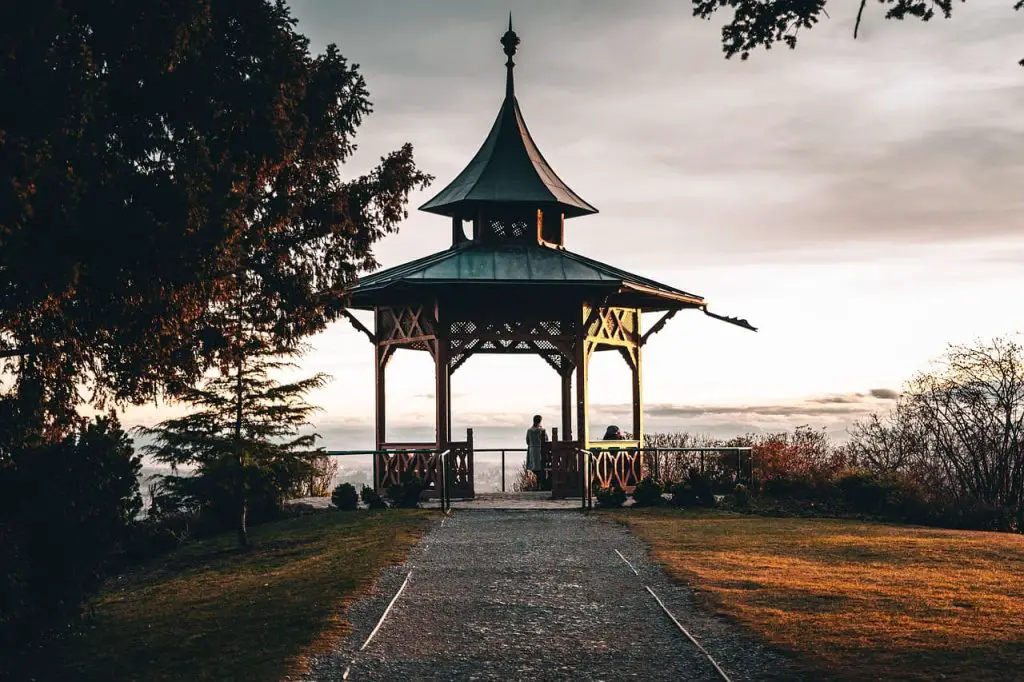

These gazebos have a square or rectangular shape, with a flat or sloping roof.
They are often used for outdoor events and can be large enough to accommodate several people.
Hexagonal gazebos
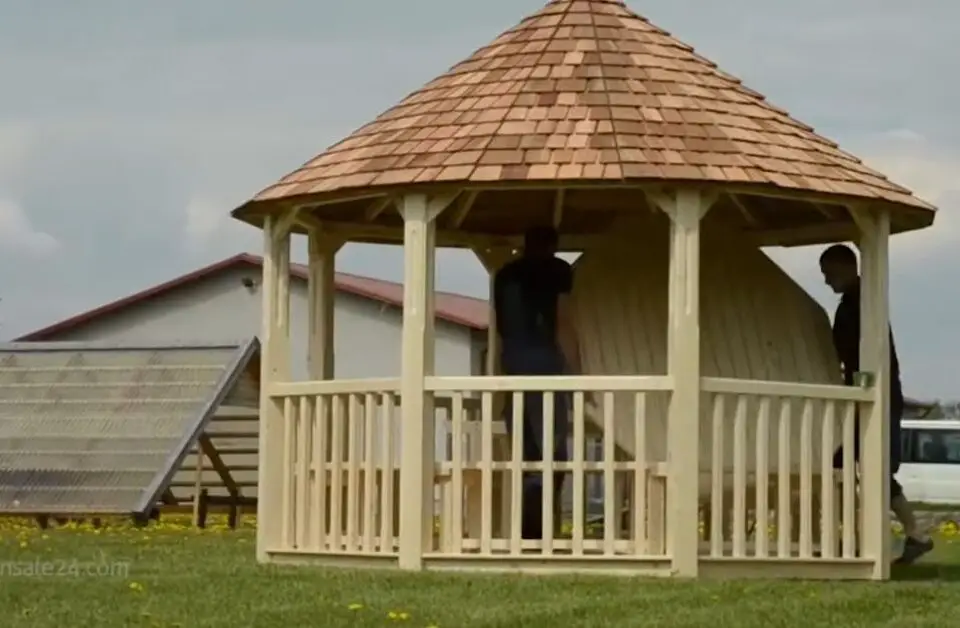

These pavilions have six sides and a roof that is typically domed.
They are smaller than pavilion gazebos and are commonly used as a decorative feature in gardens.
Victorian gazebos

These gazebos have a distinctive design with ornate details like spindles and intricate carvings.
They are often made of wood and are designed to be aesthetically pleasing.
Pergola gazebos
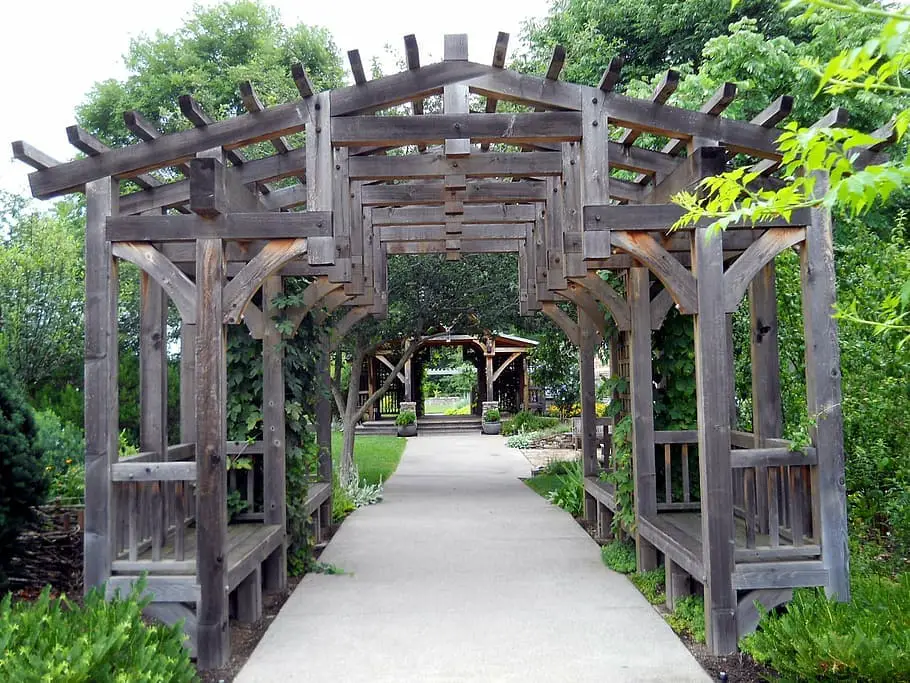

These gazebos have a flat roof and are often attached to a building or another structure.
They are designed to provide shade and can be used to create an outdoor living space.
Materials used to construct a gazebo
Gazebos can be made from various materials, including wood, metal, and vinyl. The choice of material will depend on the intended use of the pavilion, the area’s climate, and the structure’s overall design. Here are some of the most common materials used to construct gazebos:
Wood
Wood is a popular material for gazebos due to its natural look and durability. Cedar and redwood are often used because they resist rot and insect damage. Wood gazebos can be painted or stained to match the surrounding environment.
Metal
Metal gazebos are often made of aluminum or steel and are designed to be lightweight and durable. They are typically powder-coated to prevent rust and can be painted to match the surrounding environment.
Vinyl
Vinyl gazebos are a low-maintenance option that is resistant to rot, insects, and weather damage. They are typically made of PVC and can be designed to look like wood or metal.
In conclusion, a gazebo is an outdoor structure that is often freestanding, with a roof and open sides. There are different types of gazebos, including pavilion, hexagonal, Victorian, and pergola, each with unique design and functionality.
Gazebos can be made from various materials such as wood, metal, or vinyl, depending on the intended use and design of the structure.
A greenhouse is a structure designed for cultivating and protecting plants, usually made of glass or other transparent materials. It provides a controlled environment that allows plants to thrive and grow all year round, regardless of the weather conditions outside.
Greenhouses are widely used in commercial plant production, as well as for home gardening and research purposes. This article will provide an overview of greenhouses, including their definition, types, and purpose.
Definition of a greenhouse

A greenhouse is a structure designed to create a controlled environment for plant growth. It is typically made of glass or other transparent materials that allow sunlight to enter and create a warm, humid atmosphere inside.
The temperature, humidity, and ventilation inside a greenhouse can be regulated to optimize plant growth, making it possible to grow plants in environments where they would not normally thrive.
Types of greenhouses
There are different types of greenhouses, each with its unique design and functionality. Some of the most common types of greenhouses include:
Lean-to greenhouse
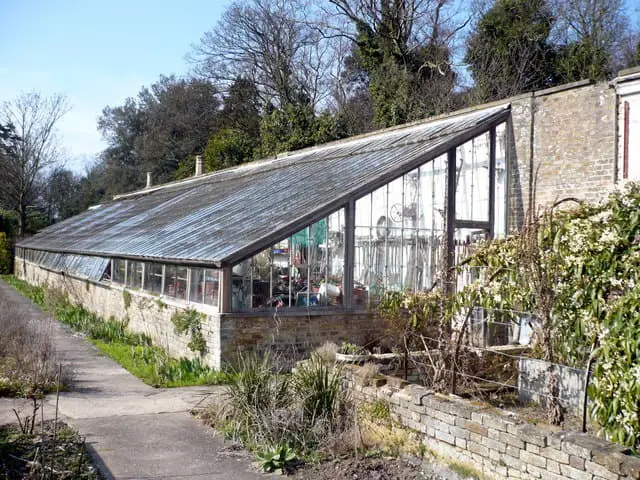

This type of greenhouse is attached to an existing structure, such as a house or garage.
It is often smaller in size and is designed to take advantage of the existing wall for support and insulation.
Free-standing greenhouse:
This type of greenhouse is freestanding and can be placed anywhere in a garden or outdoor space. It can be larger in size than a lean-to greenhouse and can be designed to meet specific needs.
Gable greenhouse
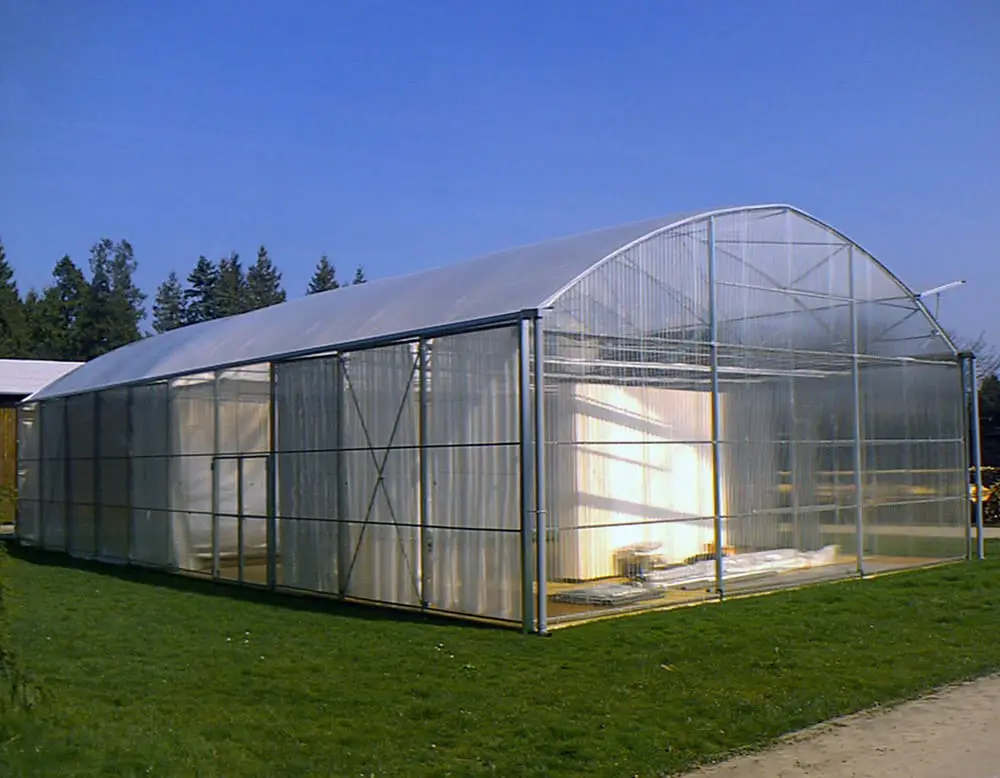

This type of greenhouse has a pitched roof with two sloping sides and a central ridge.
It is often larger than a lean-to greenhouse and provides more plant headroom and space.
Hoop greenhouse
This type of greenhouse is made of metal hoops or PVC pipes covered with a plastic or polyethylene film. It is a low-cost option that is easy to assemble and can be used for temporary or seasonal plant production.
Glass greenhouse
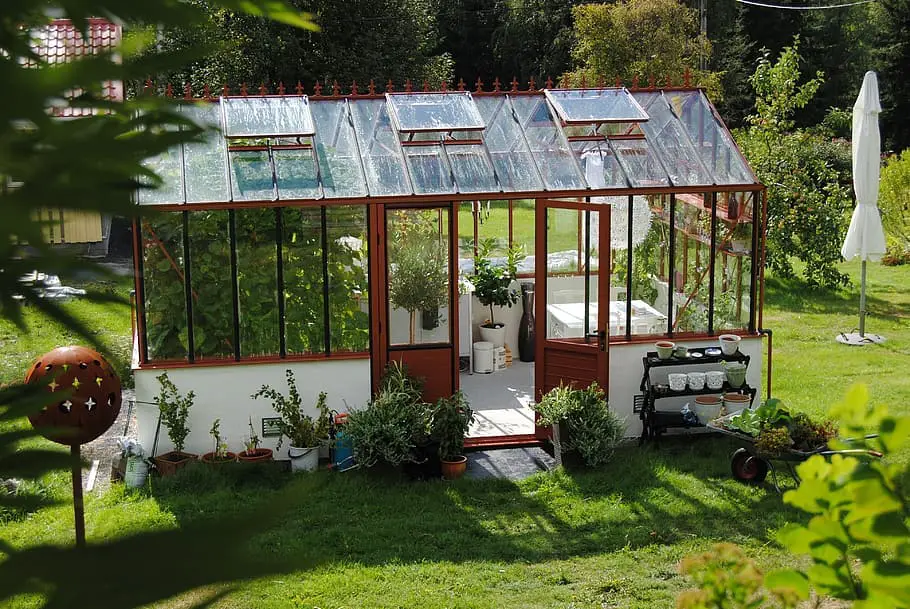

This type of greenhouse is made entirely of glass, providing excellent insulation and visibility.
It is often used for commercial plant production and requires a significant investment in construction and maintenance.
Purpose of a greenhouse
The primary purpose of a greenhouse is to provide a controlled environment for plant growth. This allows plants to grow all year round, regardless of the weather conditions outside. Greenhouses are used for a wide range of plant production purposes, including:
Commercial plant production
Greenhouses are commonly used for commercial plant production, providing an efficient and controlled environment for the growth and harvest of crops. They are used to produce fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants.
Home Gardening
Greenhouses are also used for home gardening, allowing gardeners to grow plants that would not normally thrive in their local environment. Home greenhouses can start seedlings, extend the growing season, and grow plants that require specific growing conditions.
Research and experimentation
Greenhouses are used for research and experimentation, allowing scientists to study plant growth under different environmental conditions. This research is essential for the development of new plant varieties, as well as the improvement of existing ones.
Education
Greenhouses are also used for educational purposes, allowing students to learn about plant growth and development in a hands-on environment. They can be used for school gardening programs, as well as for university-level research and training.
Can a Gazebo be used as a Greenhouse?
Gazebos are structures that are commonly used in gardens and outdoor spaces for relaxation, entertainment, and shelter from the sun or rain. They are often made of wood, metal, or vinyl and are designed to provide an open-air space with a roof and sides that are open or screened.
On the other hand, greenhouses are structures designed to create a controlled environment for plant growth.
They are typically made of glass or other transparent materials used for plant production. While gazebos and greenhouses have different functions, some people may wonder if using a gazebo as a greenhouse is possible.
we will explore the factors to consider when using a gazebo as a greenhouse and the advantages and disadvantages of this approach.
Factors to consider when using a gazebo as a greenhouse
Structure
The structure is the first factor when using a gazebo as a greenhouse. Gazebos are typically designed to provide an open-air space, meaning they may not adequately protect plants from extreme weather conditions, such as high winds or heavy rain.
In addition, gazebos may not be structurally sound enough to support the weight of glass panels or other transparent materials that are typically used in greenhouses. It is essential to assess the structural integrity of the gazebo before using it as a greenhouse.
Location
The location of the gazebo is another important factor to consider. Greenhouses require ample sunlight for plant growth, so the gazebo should be located in an area that receives sufficient sunlight throughout the day.
In addition, the gazebo should be located in an area that is sheltered from strong winds or other environmental factors that could damage the plants.
Ventilation
Ventilation is crucial for greenhouse environments, as it helps regulate temperature, humidity, and air circulation.
Most gazebos are not designed with ventilation in mind, so installing additional ventilation systems, such as fans or vents, may be necessary to ensure adequate air circulation and prevent moisture buildup.
Insulation
Insulation is also essential for greenhouse environments, as it helps regulate temperature and prevent heat loss. Most gazebos are not insulated, so it may be necessary to install additional insulation materials, such as polycarbonate sheets or bubble wrap, to provide adequate plant insulation.
Water supply
Greenhouses require a reliable water supply for plant growth. Most gazebos do not have access to a water supply, so installing a water source, such as a hose or drip irrigation system, may be necessary to provide water to the plants.
Advantages and disadvantages of using a gazebo as a greenhouse

Advantages:
Cost-effective: Using a gazebo as a greenhouse can be a cost-effective option for those who already have one and want to repurpose it for plant production.
Aesthetically pleasing: Gazebos are often aesthetically pleasing structures that can enhance the overall appearance of a garden or outdoor space.
Provides shade: Gazebos can provide shade for plants requiring partial shade, such as specific flowers or herbs.
Portable: Some gazebos are designed to be portable, which means that they can be moved to different locations as needed.
Disadvantages:
Limited space: Gazebos are typically smaller than traditional greenhouses, so they may not provide enough space for more significant plant production.
Limited protection: Gazebos may not adequately protect plants from extreme weather conditions or pests.
Limited functionality: Gazebos are not designed with greenhouse functionality in mind, so additional modifications may be necessary to provide adequate environmental conditions for plant growth.
Tips for converting a gazebo into a greenhouse
Converting a gazebo into a greenhouse can be a challenging task. Still, with the right approach and attention to detail, it can be a rewarding project that provides a unique and functional space for plant production.
Here are some tips for converting a gazebo into a greenhouse:
Assess the structure
Before converting a gazebo into a greenhouse, it is essential to assess the structural integrity of the pavilion. Make sure that the structure is sound and can support the weight of any additional materials that will be added for greenhouse functionality.
If the pavilion is not structurally sound enough, reinforcing or rebuilding the structure may be necessary.
Choose suitable materials.
The materials used in a greenhouse are crucial for creating the right environment for plant growth. Choose durable, weather-resistant materials that provide adequate insulation and ventilation.
Some materials commonly used in greenhouses include polycarbonate sheets, bubble wrap, shade cloth, and fans or vents for air circulation.
Install ventilation systems
Ventilation is crucial for maintaining a healthy and productive greenhouse environment. Make sure to install adequate ventilation systems, such as fans or vents, to regulate temperature and humidity and prevent moisture buildup.
Provide a water source.
Plants require a reliable water source for growth, so providing a water source in the greenhouse is essential. This can be done through a hose, drip irrigation system, or other watering methods.
Consider lighting
Depending on the pavilion’s location, it may be necessary to provide additional lighting to supplement natural sunlight for plant growth. Consider installing artificial lighting, such as grow lights, to provide the right amount and spectrum for plant growth.
Monitor environmental conditions
Once the pavilion has been converted into a greenhouse, it is essential to monitor environmental conditions regularly.
This includes temperature, humidity, light levels, and air circulation. Make adjustments as necessary to ensure optimal growing conditions for plants.
Choose appropriate plants
Not all plants are suitable for greenhouse environments, so choosing plants that can thrive in the specific conditions provided by the greenhouse is essential. Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, light levels, and ventilation when selecting plants for the greenhouse.
In summary, converting a gazebo into a greenhouse requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a focus on creating the right environment for plant growth.
With suitable materials, ventilation systems, and environmental monitoring, a gazebo can be transformed into a unique and functional greenhouse that provides a space for year-round plant production.
Benefits of Using a Gazebo as a Greenhouse
Using a gazebo as a greenhouse offers several benefits for gardeners and plant enthusiasts. Here are some of the main advantages:
Cost-effective alternative
Converting a gazebo into a greenhouse can be more cost-effective than building or buying a traditional greenhouse. This can be especially beneficial for those on a budget or wanting to repurpose an existing structure.
Increased accessibility
Gazebos are typically more accessible and easier to maintain compared to traditional greenhouses. This can make gardening more accessible for people who may not have the space, resources, or skills to build or maintain a traditional greenhouse.
Aesthetically pleasing
Gazebos can be aesthetically pleasing structures that can add to the overall visual appeal of a garden or backyard space. This can make the greenhouse more enjoyable to spend time in and can enhance the overall outdoor experience.
Versatility
Gazebos can be used for various purposes, from hosting outdoor events to providing shade on hot days. Converting a gazebo into a greenhouse adds to the structure’s versatility and allows for year-round use.
Overall, using a gazebo as a greenhouse offers several advantages and can be a great option for those looking for a cost-effective and accessible way to grow plants.
FAQS
Here are some frequently asked questions about using a gazebo as a greenhouse:
Q.1 Can any gazebo be converted into a greenhouse?
Ideally, a sturdy and durable gazebo would be best for converting into a greenhouse. If the pavilion is not structurally sound or made of low-quality materials, it may not be suitable for conversion.
Q.2 What materials are best for a gazebo greenhouse?
The materials used in a greenhouse are crucial for creating the right environment for plant growth. Durable, weather-resistant materials such as polycarbonate sheets, bubble wrap, and shade cloth can provide adequate insulation and ventilation.
Q.3 How do I install ventilation systems in a gazebo greenhouse?
Installing ventilation systems such as fans or vents is crucial for maintaining a healthy greenhouse environment. Professional installation is recommended to ensure proper function and safety.
Q.4 Can a gazebo greenhouse be used year-round?
A gazebo greenhouse can be used year-round with proper insulation, ventilation, and heating systems.
Q.5 Do I need special lighting for a gazebo greenhouse?
A: Depending on the pavilion’s location, it may be necessary to provide additional lighting to supplement natural sunlight for plant growth. Artificial lighting, such as grow lights, can provide the correct light spectrum for plant growth.
Q.6 What types of plants are suitable for a gazebo greenhouse?
The plants suitable for a gazebo greenhouse will depend on the specific conditions provided by the greenhouse. Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, light levels, and ventilation when selecting plants for the greenhouse.
Q.7 How do I maintain a gazebo greenhouse?
Regular monitoring of environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, light levels, and air circulation is necessary. Make adjustments as necessary to ensure optimal growing conditions for plants. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the greenhouse structure and equipment is also recommended.
Conclusion
In conclusion, using a gazebo as a greenhouse is a viable option for plant enthusiasts looking for a cost-effective and accessible way to grow plants.
Converting a gazebo into a greenhouse offers several advantages, including increased accessibility to gardening, the aesthetic appeal of a gazebo structure, and cost-effectiveness compared to a traditional greenhouse.
However, there are several factors to consider before converting a gazebo into a greenhouse, including proper insulation, ventilation, and heating systems.
With proper planning and installation, a gazebo greenhouse can be a great addition to a backyard or garden space, providing year-round plant production and enhancing the overall outdoor experience.
We hope this guide has helped you understand if a gazebo can be used as a greenhouse. If you have any questions, please feel free to comment below.